What is Your Water Footprint?
IDRA has promoted water reuse and desalination solutions for over fifty years to meet water scarcity needs. In June 2022, IDRA began its quest to advocate for a Be Water Positive + Initiative to share knowledge and spotlight actions on water stewardship.
In October 2022, IDRA created a special board committee to action further this initiative, entitled the Water +, Carbon Neutral, Environmental Stewardship Committee. The committee’s objective is to encourage the industry to implement best practices on environment and energy efficiency in all desalination and water reuse projects by using the best available and most appropriate technologies according to the location of the plants. The committee task force facilitates discussion of environmental issues associated with desalination and water reuse, with their main KPI being to advocate for environmental stewardship, recycling of water to lower the water footprint, decarbonization, implementation of increased renewable power in plant operations, and reduction of chemical consumption. In addition to advocating for overall sustainability that balances activities cohesively and collaboratively with the local water resource, emphasizing the “Value of Fresh Water Resources” and the importance of environmental stewardship to protect them.
Fortunately, global companies are increasingly seeing the economic and environmental advantages of adopting environmental, social, and governance (ESG) philosophies. ESG criteria are fast becoming a fundamental pillar of corporate strategy. The commitment to be Water Positive+ is not a matter of individual reputation but rather a planned phase of the operation that will help companies achieve long-term objectives of aligning themselves with the United Nations Sustainability Goals. It is no longer enough to Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle; to achieve a water positive + balance, we need to recover and return more water than we use in our production processes. Thanks to new regulations and technological advances in water purification solutions and alternative energies, non-conventional water sources, specifically desalination and water reuse are now positioned as the leading option to supply natural water resources, delivering high purity water.
IDRA Be Water Positive+
For the IDRA, being water positive means compensating for your water footprint by producing high-quality water and reducing water consumption. Scientific evidence shows that rainwater harvesting can prove to be a useful method of being water positive+. Although it has pros and cons, evidence shows that the only differentiator contributing to the result is the implementation of specific systems. However, this can be done more efficiently through desalination and water reuse. Therefore, desalination and water reuse are effective means of helping the natural water cycle. While industries remain steadfast in producing goods, food, and services at a high rate – only by being water positive+ can we create impact where it matters most.
Water Footprint

A water footprint is the amount of freshwater utilized in producing or supplying the goods and services used by individuals, communities, and companies.
Assessment of Water Footprints
While the ISO 14046:2014 standard provides principles, requirements, and guidelines for assessing, conducting, and reporting a water footprint, it does not report on water footprint results, like a label or a declaration.
Some well-known water footprint certifications are:
Components of a Water Footprint

- Green water footprint: precipitated water that is stored in the root zone of the soil and is evaporated, transpired, or incorporated by plants.
- Blue water footprint: water from surface or groundwater resources that is incorporated into a product or is taken from one body of water and returned to another body of water or is returned at a different time.
- Grey water footprint: the volume of freshwater required to assimilate pollutants based on natural background concentrations and existing ambient water quality standards
Water Footprints by Country
An example of this would be the areas shaded in green, depicting where the nation’s water footprint is equal to or less than the world average. Similarly, the countries in red depict a higher water footprint than the world average
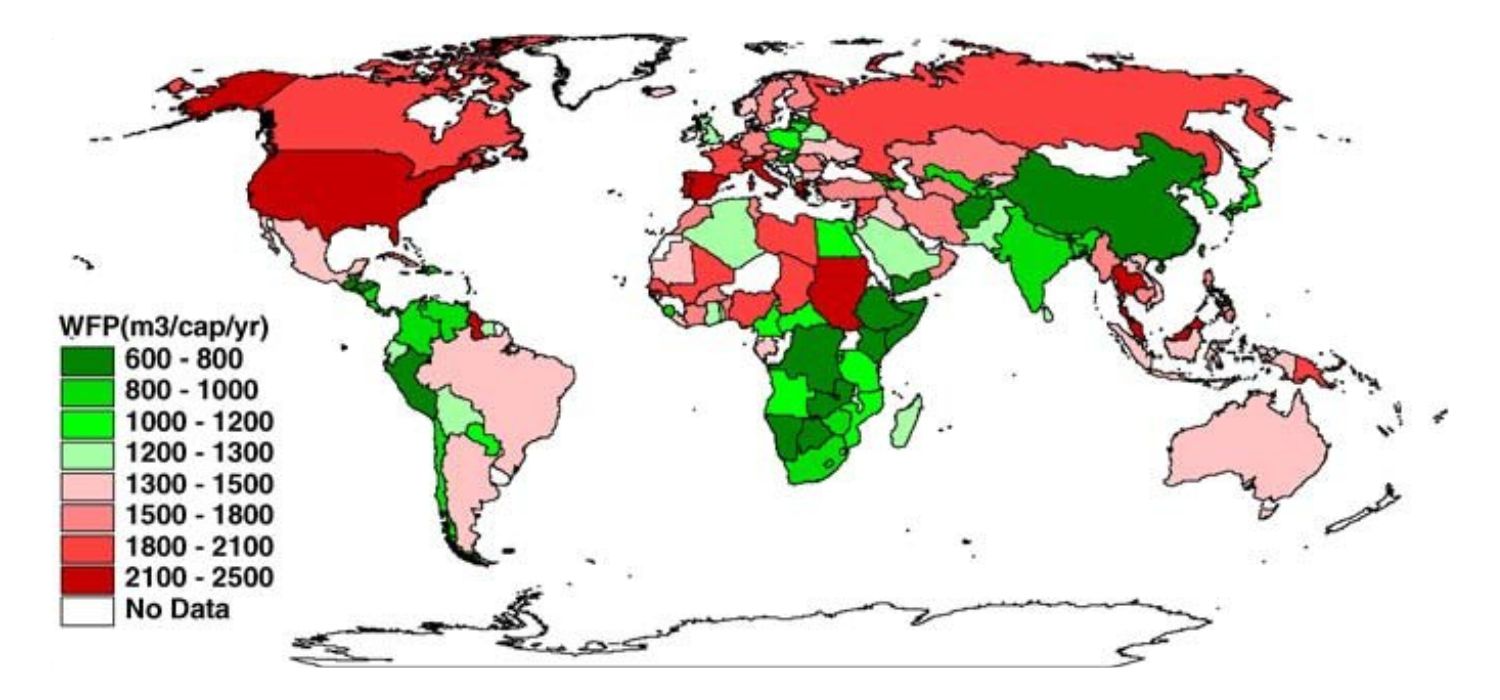
GWSP Digital Water Atlas (2008). Map 33: Water Footprint per Country (V1.0). Available online at http://atlas.gwsp.org.
Water footprints vary between countries due to people’s consumption habits, climate, and water use practices. An example of this would be the areas shaded in green, depicting where the nation’s water footprint is equal to or less than the world average. Similarly, the countries in blue depict a higher water footprint than the world average.
The map shows you the average national water footprint per capita (m3 / person / year) by people based on their consumption patterns.
Components of a Water Footprint
• Green water footprint: precipitated water that is stored in the root zone of the soil and is evaporated, transpired, or incorporated by plants
• Blue water footprint: water from surface or groundwater resources that is incorporated into a product or is taken from one body of water and returned to another body of water or is returned at a different time.
• Grey water footprint: the volume of freshwater required to assimilate pollutants based on natural background concentrations and existing ambient water quality standards.
Water Footprints by Industry

We know that water is a vital source for operations in many industries. According to the McKinsey & Company Report: The global corporate water footprint, by 2030 water demand will outstrip supply by 40% and about half of the world’s population will live in water-scarce areas. This means industries will face more public and regulatory scrutiny about water usage, especially in water-scarce areas.
Corporate water users are starting to understand the severity of the water crisis or its eventual impact on their business by assessing their water footprint and the water footprint of their suppliers.
Net Zero

The goal of water positive + is to minimize the negative impact associated with usage of our natural water resources.
The objective of water positive pledges by companies align with the UN’s goals of adequate access to clean water for all while securing their water supply needs. Water security is a local issue that can be improved by reducing water consumption and replenishing water resources through recycling.
Negative impacts can be reduced by utilizing desalination and water reuse as a water source or even supporting local governments in the environmental restoration of watersheds.
Learn more about IDRA Be Water Positive
IDRA signs MOU with Canada Ocean Racing Water Positive IMOCA Team

Articles, Reports and Tools
Explore the articles and insights from water industry experts on the IDRA Be Water Positive+ initiative. Gain valuable knowledge and perspectives from seasoned professionals in the field as they delve into the intricacies of this groundbreaking initiative, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of its impact and significance within the water industry.
- On the Road to Water Positive – Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- On the Road to Carbon Neutrality – Al Taweelah Reverse Osmosis (RO) Treatment Plant
- On the Road to Be Water Positive – Google
- On the Road to be Water Positive – P&G
- Water Positive, the Time for Water ESG Criteria
- To March to Net Zero and Water Positive (NZ&W+) | Real End Users Experiences
- Industrial Water’s New Future: The Challenges and Opportunities in Moving to Net Zero and Water Positive
- Beyond Neutrality, Towards Positive Impact: The Water Positive Initiative
- Freshwater Ecosystems Explorer
- OpenET
- Global Water Watch
- BlueConduit
- CDP Supply Chain
Awards
IDRA World Congress Industry and Sustainability Award Nominations Open Now!
The IDRA awards call to nominations open August 2024. The awards will be presented at the IDRA World Congress 2024 in Abu Dhabi, graciously hosted by the Abu Dhabi Department of Energy.
Subscribe to stay informed
Shortest way to explore what’s happening in IDA and the global advanced water treatment community



