Published on IDRA Global Connections Spring 2021 Issue
By Mr. Jeff Mosher, General Manager of the Santa Ana Watershed Project Authority (SAWPA)
The Inland Empire Brine Line (Brine Line), located in southern California (USA), is a unique and indispensable salinity management resource for the Santa Ana River Watershed). The Brine Line, which is owned and operated by the Santa Ana Watershed Project Authority (SAWPA), supports economic growth in a semi-arid area with limited water resources by providing a regional facility for exporting salt from inland areas to the ocean.
SAWPA, a public agency, was formed in 1972 after countless lawsuits over water supply in the Watershed.SAWPA provides a forum for water agencies, regulators, and stakeholders to discuss and address issues impacting the region, including approaches to manage salinity in the Watershed.
Salinity Management
The Watershed has had historical struggles of high concentrations of total dissolved solids (TDS). Spanning west from inland Southern California to the coast of the Pacific Ocean, the Watershed has been a location of intense agricultural practices, including dairy farm and crop irrigation, which has increased salt concentrations in the region’s aquifers. In addition, imported water supply in the region from the Colorado River Aqueduct has further driven the salt imbalance. As salt levels in the groundwater rise, the potential to make use of local groundwater sources becomes more limited, posing a risk for the water supply reliability in the Watershed.
Wastewater treatment plants in inland areas in California have strict TDS restrictions to protect water quality from being degraded by high levels of salts, thereby supporting the ability to recycle water for nonpotable uses and groundwater augmentation purposes. With nowhere to dispose of their concentrates and brines for treatment, water agencies and businesses need an economical approach for managing these flows.
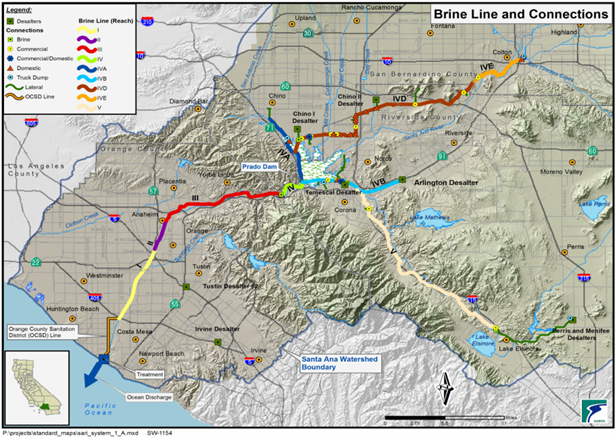
Brine Line
To support the brine management needs of water agency desalters and other high salinity dischargers from commercial and industrial facilities, the Brine Line was
constructed in the 1990s. The Brine Line provides a cost-effective, sustainable means of disposal of brines and non-reclaimable flows. The Brine Line with a capacity of
30 MGD spanning 93 miles across the Watershed collects and treats brines and high salinity flows from businesses and water agencies. Treatment of these flows occurs at the Orange County Sanitation District (OC San). Treated wastewater is then safely discharged into the Pacific Ocean.
The Brine Line with a capacity of 30 MGD spanning 93 miles across the Watershed collects and treats brines and high salinity flows from businesses and water agencies.
Groundwater Desalters Discharging Brine to the Brine Line
- Chino Desalter
- Chino Desalter II
- Temescal Desalter
- Perris Desalter
- Arlington Desalter
- Menifee Desalter
Industrial Dischargers to the Brine Line
- Biotech Manufacturing
- Power Plants/Co-Generation Plants
- Medical Supply Manufacturing
- Water Purification Plants
- Computer Chip Manufacturers
- Commercial Laundries
- Food/Beverage Processing
The Brine Line was developed using a cooperative approach between several water agencies – San Bernardino Valley Municipal Water District (MWD), Eastern MWD, Western MWD, Inland Empire Utilities Agency, and OC San. Under an integrated watershed management plan, these partnering agencies collectively constructed the watershed-wide desalination system. These desalination facilities connected to the Brine Line for brine disposal. Construction of the Brine Line was executed using loans from a novel partnership model, which were repaid using revenue generated from the customers using the Brine Line. To continue operation and maintenance of the Brine Line, funds from revenue and usage rate-generated capital reserves are utilized.
A variety of water-intensive industries and businesses use the Brine Line to dispose of their salty wastewater. To dispose of their brine, businesses can use Trucked Disposal to a collection station or Direct Disposal, a direct connection to the Brine Line.
Brine Line customers also have a cost advantage over those located outside of the watershed. Based on the volume, biochemical oxygen demand concentration, and total suspended solids concentration, partnering businesses can dispose their brines at approximately $0.05 per gallon. Compared to brine disposal rates of up to $0.25 per gallon elsewhere in the region, Brine Line customers can realize up to 500% reduction in costs.
Brine Line and Desalination Facilities in Watershed
Future of the Brine Line
Future plans for the Brine Line consist of continual operation, maintenance and rehabilitation of the desalination system to provide an economical approach to brine disposal for agencies and businesses and to meet the region’s long-term goal of achieving a workable salt balance. The Brine Line provides an economical option to accommodate the expansion of desalters and support businesses in the region with brine management needs.